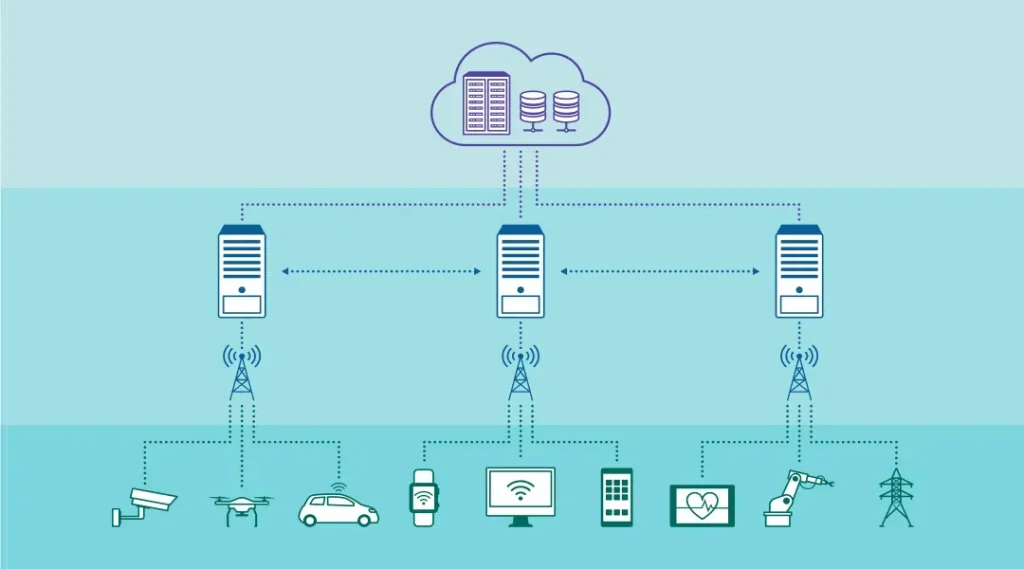
Edge Computing and 5G are redefining how data is processed at the edge, bringing computation closer to where it’s generated and consumed while reducing backhaul strain and enabling smarter, more responsive applications across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and smart cities, where milliseconds can make the difference between a closed loop and a missed opportunity, and this approach supports offline operation and event-driven workflows that fire actions without constant cloud polling. This powerful pairing enables ultra-low latency for critical workflows, real-time analytics on streaming data, better privacy by keeping sensitive data local, and more reliable data flows across edge devices, gateways, and micro data centers that sit near the places where value is created and decisions are made, while also reducing energy use during outages. As organizations scale these capabilities, they study future technology trends edge computing to understand how AI inference, orchestration, and context-aware processing can operate at the edge in energy-efficient ways without compromising security or governance, and to anticipate how distributed AI models will evolve alongside network evolution. Real-world deployments reveal 5G edge computing use cases across industries—from automated manufacturing lines that monitor equipment in real time to autonomous vehicles that rely on rapid perception and local decisioning, reducing dependence on distant cloud resources and enabling more resilient operations. IoT edge computing and cloud and edge computing 5G networks demonstrate complementary patterns, showing how localized processing can deliver immediate insights while still leveraging cloud-scale analytics, periodic model updates, and centralized control when tasks require broader context or machine-learned insights.
Describing the same shift with Latent Semantic Indexing principles, professionals speak in terms such as perimeter computing, edge-native processing, MEC (multi-access edge computing), fog computing, and on-site analytics. In practice, this means distributing compute closer to devices and sensors, enabling rapid decision-making even when connections to centralized data centers are limited. These patterns emphasize resilient architectures, clear data governance, interoperable services, and the orchestration of heterogeneous resources across networks. In short, the emphasis is on localized intelligence, scalable deployment at the network edge, and the seamless integration of edge resources with traditional cloud platforms.
Edge Computing and 5G: A Synergistic Leap for Real-Time Analytics
Edge Computing and 5G combine to redefine how data is processed, moving computation closer to the source to deliver near-instant insights and reduced backhaul. With ultra-fast networks and localized processing, organizations can run complex analytics at the edge, shortening feedback loops and enabling more responsive applications across manufacturing, retail, and transportation. This synergy supports real-time decision-making, supports immersive experiences, and lowers the risk of data overload on centralized data centers.
As devices generate massive streams of data—from sensors on factory floors to AR/VR interfaces—the edge-augmented approach helps preserve bandwidth and improve privacy by keeping sensitive information nearer to origin points. The result is a more resilient architecture where latency-sensitive tasks like anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and on-site analytics can operate independently of distant clouds, while still tapping into cloud-based models when deeper analysis is required.
Reducing Latency and Enhancing Reliability with Edge Nodes and 5G
Latency is a critical metric for applications such as autonomous control, real-time monitoring, and interactive experiences. By deploying computation at edge nodes and leveraging 5G’s low-latency, high-bandwidth transport, networks can guarantee more consistent performance even during peak loads. Network slicing and quality-of-service guarantees further ensure that critical workloads receive the necessary resources when needed.
Edge computing use cases in 5G-enabled environments showcase how localized processing accelerates response times, enables rapid data fusion, and supports bursty data traffic without burdening central clouds. In sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and smart mobility, edge-enabled tasks—ranging from real-time analytics to secure local inference—benefit from the synergy of 5G networks and edge infrastructure.
IoT Edge Computing in the Enterprise: Governance, Privacy, and Scale
IoT edge computing distributes intelligence across devices, gateways, and local servers to empower enterprises with operational insights while keeping control over data. This distributed model helps manage data residency, latency targets, and device diversity, enabling scalable deployments across facilities, campuses, and cities. A well-planned edge strategy aligns data flows with business objectives and supports governance policies tailored to edge environments.
Security and interoperability are foundational to successful IoT edge programs. Implementing secure boot, encrypted channels, attestations, and robust key management at edge nodes builds trust and resilience. By designing interoperable data pipelines and open standards, organizations can avoid vendor lock-in and facilitate seamless collaboration between on-premises systems, edge clusters, and cloud services.
Industry Use Cases Across Sectors: Manufacturing, Mobility, and Healthcare
The marriage of Edge Computing and 5G unlocks diverse use cases across industries. In manufacturing, real-time anomaly detection and predictive maintenance minimize downtime, while local data processing supports responsive automation and quality control. For mobility, autonomous vehicles and smart fleets rely on edge-enabled perception and low-latency communication to improve safety and efficiency.
Healthcare and retail also benefit from on-site analytics and edge-assisted workflows. Telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and AR-assisted procedures can operate with faster, privacy-preserving data processing at the edge. Across retail and public services, edge analytics drive personalized customer experiences and real-time inventory visibility, powered by the convergence of edge compute and 5G connectivity.
Future Technology Trends Edge Computing: AI, Security, and Orchestration
Looking ahead, AI and machine learning are moving toward the edge, enabling local inference and, in some cases, on-device training to reduce data movement and privacy risk. This aligns with the broader concept of future technology trends edge computing, where intelligent agents operate closer to data sources, delivering faster, context-aware insights.
Security, orchestration, and automation are also maturing at the edge. Hardware isolation, secure enclaves, and encrypted data pathways strengthen defenses against threats, while edge-native platforms, lightweight containers, and orchestration tools simplify deployment, updates, and lifecycle management for heterogeneous devices. Energy efficiency and sustainable operation remain high priorities as networks scale and edge ecosystems expand.
Hybrid Cloud and Edge in the 5G Era: Architectures, Offloading, and Network Slicing
The modern stack blends cloud capabilities with edge resources, connected by pervasive 5G networks to form hybrid architectures that adapt to varying workload requirements. Tiered processing and intelligent offloading enable applications to run at the most appropriate location, whether on local edge nodes for immediacy or in the cloud for deeper analytics and model training.
Operators can leverage network slicing to guarantee performance for critical workloads while allowing best-effort processing for less time-sensitive tasks. This approach, coupled with multi-vendor interoperability and robust data routing strategies, supports rapid scaling, improved user experiences, and a lower total cost of ownership as organizations optimize resource utilization across cloud and edge environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 5G edge computing use cases and how does Edge Computing enable them?
5G edge computing use cases span industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, AR/VR, and healthcare. Edge computing brings processing closer to devices, reducing latency, saving bandwidth, and enabling real-time insights. When combined with 5G, ultra-fast connectivity and network slicing ensure predictable performance for time-critical workloads.
How do cloud and edge computing 5G networks work together to deliver superior performance?
They form a hybrid architecture where edge computes near data sources for low latency, while the cloud provides deep analytics, storage, and model training. 5G networks with network slicing and high throughput tie the layers together, enabling responsive applications and scalable offloading as needed.
How does IoT edge computing leverage 5G networks to enable real-time insights?
IoT edge computing distributes intelligence to devices, gateways, and local servers, pushing processing closer to data sources. 5G networks deliver speed and capacity to move data quickly to and from edge nodes, supporting real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and privacy-preserving analytics.
What are the future technology trends edge computing that are accelerated by 5G?
Key trends include AI/ML at the edge, secure enclaves and privacy-preserving processing, edge orchestration with lightweight containers, and energy-efficient offloading. 5G provides ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable connectivity that sustain edge workloads across distributed deployments.
How do cloud and edge computing 5G networks enable scalable, hybrid architectures?
This approach blends edge compute for latency-sensitive tasks with cloud analytics for longer-term insights. 5G network slicing guarantees performance for critical workloads while allowing flexible offloading between edge and cloud, helping organizations scale with lower total cost of ownership.
What security and interoperability considerations are essential for Edge Computing and 5G deployments, including IoT edge computing?
Plan for secure boot, encrypted channels, device attestation, and robust key management across distributed nodes. Establish data governance, privacy protections, and vendor interoperability with open standards to avoid lock-in, especially as IoT edge computing expands the edge deployment.
| Key Point | Description | Benefits | Examples / Use Cases | Notes / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Edge computing moves data processing closer to data sources (edge devices, gateways, micro data centers) while 5G provides high speeds and low latency. | Reduced latency, bandwidth efficiency, real-time insights. | Autonomous machines; AR/VR; smart cities. | Edge nodes include edge devices, gateways, micro data centers; near-source processing is the core idea. |
| Synergy of Edge + 5G | Ultra-fast data processing at the edge enabled by robust 5G networks, enabling instant decisions and localized processing. | Faster response times, improved reliability, bandwidth efficiency. | Industrial automation; autonomous vehicles; smart mobility; AR/VR. | Network slicing and QoS guarantees help ensure performance for diverse workloads. |
| Why it matters today | Latency, bandwidth, and reliability are critical; traditional cloud routing adds delays. Pushing compute toward the edge reduces round trips. | Near-instant responses, better privacy, and higher resilience. | Real-time analytics; industrial automation; immersive experiences; healthcare and telemedicine; smart retail. | Balance edge and cloud; design for security and privacy from the start. |
| Representative Use Cases | A broad set of use cases across industries where edge + 5G enables local processing and quick decision-making. | Operational efficiency, safety, and enhanced user experiences. | Industrial automation; autonomous vehicles; smart cities; AR/VR for enterprises; healthcare and telemedicine; retail and customer experience. | Edge + 5G enables local data processing with cloud analytics when needed; plan for governance and interoperability. |
| Future Trends | AI/ML at the edge; security and privacy embedded in edge architectures; orchestration and lightweight edge platforms; energy efficiency. | Localized intelligence, reduced data movement, and sustainable processing. | Edge AI inference; secure enclaves; edge-native platforms for deployment and updates. | Standardization, hardware-software integration, and vendor-agnostic edge stacks are important for scale. |
| Implementation & Governance | Define objectives: latency targets, data residency, and where edge intelligence is applied; plan edge pipelines. | Structured adoption, security by design, and manageable risk. | Edge-native stacks; lightweight containers; microservices; edge orchestration tools. | Open standards; multi-vendor strategies; interoperability; data governance and access controls. |
| Cloud & Edge in the 5G Era | Modern networks blend cloud capabilities with edge resources, connected by pervasive 5G reach; design for flexible data routing and offloading. | Scalability, faster time-to-value, optimized resource utilization, and lower total cost of ownership. | Task offloading; tiered processing; central analytics; hybrid workloads. | Network slicing enables dedicated performance for critical workloads; plan for edge-to-cloud orchestration. |
Summary
Edge Computing and 5G are rewriting how organizations collect, process, and act on data at the edge. This descriptive overview highlights how moving computation closer to devices, combined with ultra-reliable, high-speed networks, enables near-instant insights, smarter operations, and resilient digital experiences across industries. By integrating edge sites, orchestration, and network slicing in 5G-enabled environments, businesses can balance real-time responsiveness with scalable cloud analytics, while maintaining security and data governance. As adoption grows, developers, operators, and end users will benefit from more immersive experiences, safer autonomous systems, and smarter cities—driven by the continued convergence of Edge Computing and 5G.