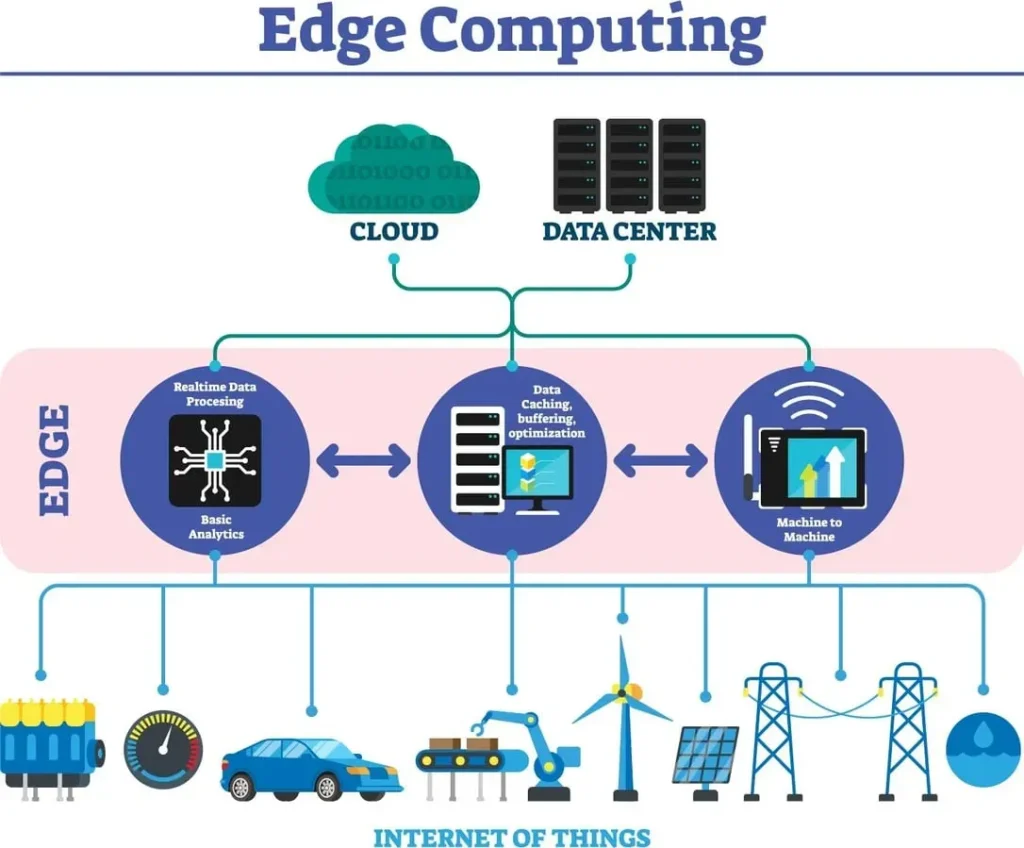
Edge Computing is no longer a niche technology; it has become the backbone of the modern digital era, powered by 5G edge computing. As networks roll out globally and generate vast amounts of real-time data, organizations face a critical question: where should processing happen to deliver the fastest experiences? Edge Computing embraces a distributed model that moves compute closer to data sources and enables AI at the edge for real-time intelligence. By placing processing near devices, businesses can cut latency, improve bandwidth efficiency, and unlock capabilities across industries with edge data centers serving as local hubs. In short, this paradigm reshapes digital infrastructure and enables faster, more secure experiences at the edge.
Think of this shift in terms of localized processing and near-edge analytics that bring compute closer to devices. In Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)-inspired language, you’ll hear phrases like near-edge processing, distributed edge computing, and edge-cloud collaboration, all signaling a move toward low-latency insights at the source. The idea is to keep data closer to users while still leveraging cloud-like capabilities through modular, orchestrated edge resources. Together, these terms describe a resilient, responsive architecture that supports real-time AI and autonomous decision-making at the edge.
Edge Computing in the 5G Era: Unlocking Ultra-Low Latency and Local Intelligence
As 5G networks continue to proliferate, Edge Computing emerges as the practical home for real-time processing, storage, and inference close to where data is created. This convergence enables ultra-low latency and highly responsive services by distributing compute resources to edge nodes, micro data centers, and on-premises devices. The result is a more capable and resilient network that supports latency budgets and bandwidth efficiency, while leveraging edge network architecture to optimize data flows.
By embracing 5G edge computing, organizations can minimize backhaul traffic and accelerate decision-making at the edge. Local processing supports real-time analytics, faster AI-driven insights, and privacy-preserving data handling, all facilitated by edge data centers and optimized networking. This edge-forward approach reshapes traditional infrastructure to deliver faster, more reliable experiences across industries.
AI at the Edge: Real-Time Intelligence When Data Is Born
AI at the edge brings intelligence directly to the devices and edge nodes where data originates. Local inference reduces the need to shuttle raw data to distant clouds, decreasing latency and boosting privacy by keeping sensitive information near its source. Edge devices and micro data centers work in concert to deliver smart, context-aware responses in real time.
With AI at the edge, enterprises can deploy lightweight, optimized models that adapt to local conditions, enabling anomaly detection, personalized interactions, and rapid decision-making in remote locations. The combination of edge data centers and edge-aware AI accelerators supports scalable architectures that minimize centralized bottlenecks while expanding capabilities across the network.
From Cloud-Centric to Cloud-Edge: Building a Hybrid Edge Network
The traditional cloud-centric model is evolving into a cloud-edge continuum where workloads migrate between the cloud and the edge based on latency requirements, data sovereignty, and cost considerations. This hybrid paradigm augments the cloud with edge resources, enabling responsive applications without sacrificing centralized training and long-term storage.
A well-designed cloud-edge strategy uses lightweight edge nodes for immediate processing while deferring heavy ML training and archival tasks to centralized data centers. This balance ensures resilience, continuous service during connectivity fluctuations, and a more flexible architecture that aligns with edge network architecture principles.
Designing Edge Network Architecture for Resilience and Scale
Architecting for the edge requires attention to latency budgets, tiered computing, open standards, and interoperable platforms. Edge network architecture should enable seamless orchestration across distributed sites, ensuring workloads can move quickly between edge nodes, regional data centers, and the cloud. Prioritizing modular, container-based deployment helps maintain consistency and scalability.
Beyond technology, this design emphasizes data governance close to data sources, privacy-preserving techniques, and robust security. By mapping data flows and enforcing standard interfaces, organizations reduce complexity, improve reliability, and support faster time-to-value for edge initiatives, while maintaining strong governance and compliance.
Security and Governance at the Edge: Zero-Trust and Compliance
Edge deployments expand the attack surface, making proactive security essential. Implementing a zero-trust architecture at the edge means authenticating and authorizing every request, regardless of origin, and continuously verifying device trustworthiness. Edge security practices must guard both data in transit and at rest, leveraging hardware-backed protections and secure boot processes.
Real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and rigorous software supply chain integrity are critical to maintaining trust at scale. By validating updates, signing software, and auditing edge activities, organizations can detect compromises early and maintain resilient operations across distributed edge sites.
Operational Best Practices for 5G-Enabled Edge Deployments
Starting with a well-defined use case helps ensure edge initiatives deliver measurable latency, bandwidth, and privacy benefits. Data flow mapping clarifies where processing should occur—at the edge, in the cloud, or somewhere in between—and guides incremental deployment through controlled pilots that scale over time.
A successful edge program requires a thoughtful vendor and partner strategy, open and interoperable platforms, and a focus on skills development. Investing in training for edge developers, architects, and operators—along with clear governance and performance metrics—ensures that organizations can realize the full value of 5G edge computing, AI at the edge, and edge data centers while maintaining low-latency networking and robust security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is edge computing and how does 5G edge computing enhance low-latency networking?
Edge computing brings compute and storage closer to data sources, enabling faster responses. When combined with 5G edge computing, processing happens near devices and endpoints, delivering ultra-low latency and improved reliability through low-latency networking. Edge data centers and edge network architecture support local analytics and reduced backhaul traffic.
How does AI at the edge influence decision-making within an edge network architecture?
AI at the edge runs inference locally on edge nodes or micro data centers, reducing data sent to the cloud, lowering latency, and enabling real-time decisions. This distributes intelligence across the network and strengthens edge network architecture while improving privacy.
What is the role of edge data centers in a cloud-edge continuum?
Edge data centers provide localized compute, storage, and networking near users, serving as the bridge in a cloud-edge continuum. They support latency-sensitive workloads, support faster analytics, and help enforce data governance, while the cloud handles training and long-term storage.
What security considerations are essential for edge computing in low-latency environments?
Key security practices include zero-trust architecture, security-by-design at the edge, encryption in transit and at rest, hardware-backed security modules where possible, secure boot, tamper detection, and real-time monitoring. These controls help protect distributed edge sites within low-latency networks.
How should organizations design an edge network architecture to scale workloads effectively?
Design with clear latency budgets, implement a tiered computing strategy using edge nodes and regional data centers, favor open standards and interoperable hardware, deploy scalable edge orchestration, and apply data governance close to the data source to simplify management and reduce risk.
What are practical use cases for edge computing in industries like manufacturing and autonomous mobility?
Practical uses include real-time process control and predictive maintenance in manufacturing, and vehicle-to-infrastructure data exchanges in autonomous mobility. AI at the edge and edge data centers enable real-time analytics, low-latency decision-making, and privacy-preserving processing across these domains.
| Key Concept | Summary | Benefits / Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Computing: Definition and Purpose | Places compute, storage, and intelligence closer to data sources to reduce latency and enable real-time insights. | Lower latency; improved bandwidth efficiency; privacy; real-time analytics; more responsive applications. |
| Edge & 5G Relationship | Edge and 5G are complementary; 5G enables ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity while the edge processes data near devices. | Faster, more reliable services; reduced backhaul traffic; better orchestration across devices. |
| Cloud-Edge Continuum | Hybrid architecture where workloads migrate between cloud and edge; edge handles immediacy; cloud handles training and long-term storage. | Flexibility, resilience, and optimized cost; seamless workload migration. |
| Core Components | Edge nodes/micro data centers; Edge orchestration; AI at the edge; Fog computing and cloud-edge continuum; Networking and security at the edge. | Clear roles; scalable deployments; privacy-preserving analytics; better security posture. |
| Industry Use Cases | Manufacturing (real-time control, predictive maintenance); Autonomous mobility (V2X); Smart cities (traffic, safety); Healthcare (remote monitoring, real-time imaging). | Real-time decisions, improved safety, operational efficiency, privacy/compliance benefits. |
| AI at the Edge | Inference runs locally, reducing cloud bandwidth, lowering latency, and enhancing privacy. | Faster decisions, privacy, scalable architectures, and local analytics. |
| Architecture, Security, and Operations | Design for latency budgets; tiered computing; open standards; scalable edge orchestration; data governance near sources. | Predictable performance, interoperability, governance, and resilience. |
| Path Forward | 5G-enabled Edge Computing will unlock new business models and AI-enabled capabilities; blends on-premises, regional, and cloud resources. | Future-proofed infrastructure; agility; new revenue streams. |
Summary
Edge Computing, in tandem with 5G, is redefining how organizations design and deploy technology infrastructure. By moving compute closer to data sources, it delivers lower latency, bandwidth efficiency, and enhanced privacy, enabling real-time analytics and smarter applications at the edge. The cloud-edge continuum fosters a flexible, resilient architecture where workloads flow between edge nodes and cloud resources, optimizing performance and cost. As AI accelerators, open standards, and disaggregated hardware mature, Edge Computing will empower more intelligent, autonomous systems across industries, from manufacturing floors to intelligent cities. Embracing this transition now helps organizations innovate faster, respond to changing conditions more effectively, and deliver experiences previously impossible with a cloud-centric model.